how to find current ratio
Current Ratio Meaning
The current ratio is a liquidity ratio that indicates a company's capacity to repay short-term loans that are due within the next year. It answers the question: "How many dollars in current assets are there to cover each dollar in current liabilities?
You are free to use this image on your website, templates etc, Please provide us with an attribution link Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Current Ratio (wallstreetmojo.com)
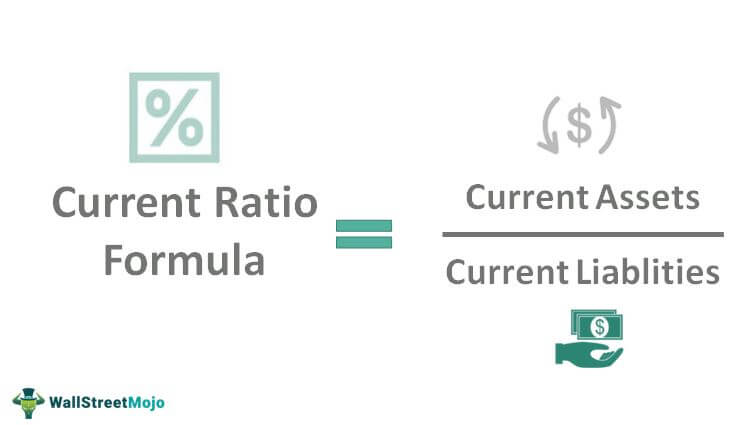
Current Ratio Formula
Current Ratio Formula = Current Assets / Current Liablities.
If for a company, current assets are $200 million and current liability is $100 million, then the ratio will be = $200/$100 = 2.0.
| Current Assets | Current Liabilities |
|---|---|
| Cash & cash equivalents | Accounts Payable Accounts payable is the amount due by a business to its suppliers or vendors for the purchase of products or services. It is categorized as current liabilities on the balance sheet and must be satisfied within an accounting period. read more |
| Investments | Deferred Revenues Deferred Revenue, also known as Unearned Income, is the advance payment that a Company receives for goods or services that are to be provided in the future. The examples include subscription services & advance premium received by the Insurance Companies for prepaid Insurance policies etc. read more |
| Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable | Accrued Compensation |
| Notes receivable Notes Receivable is a written promise that gives the entitlement to the lender or holder of notes to receive the principal amount along with the specified interest rate from the borrower at the future date. read more maturing within one year | Other accrued expenses An accrued expense is the expenses which is incurred by the company over one accounting period but not paid in the same accounting period. In the books of accounts it is recorded in a way that the expense account is debited and the accrued expense account is credited. read more |
| Other receivables | Accrued Income Taxes |
| Inventory of raw materials Raw materials inventory is the cost of products in the inventory of the company which has not been used for finished products and work in progress inventory. Raw material inventory is part of inventory cost which is reported under current assets on the balance sheet. read more , WIP, finished goods | Short Term notes |
| Office supplies | Current Portion of Long term debt |
| Prepaid expenses | |
| Advance payments |
Interpretation of Current Ratios
- If Current Assets > Current Liabilities, then Ratio is greater than 1.0 -> a desirable situation to be in.
- If Current Assets = Current Liabilities, then Ratio is equal to 1.0 -> Current Assets are just enough to pay down the short term obligations.
- If Current Assets < Current Liabilities, then Ratio is less than 1.0 -> a problem situation at hand as the company does not have enough to pay for its short term obligations.
Current Ratio Example
Which of the following companies is in a better position to pay its short term debt?
| Particulars | Company A | Company B | Company C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current Assets | 300 | 160 | 400 |
| Current Liabilities | 200 | 110 | 180 |
| Current Ratios | 1.50 | 1.45 | 2.22 |
From the above table, it is pretty clear that company C has $2.22 of Current Assets for each $1.0 of its liabilities. Company C is more liquid and is apparently in a better position to pay off its liabilities.
However, please note that we must investigate further if our conclusion is actually true.
Let me now give you a further breakup of Current Assets, and we will try and answer the same question again.
| Particulars | Company A | Company B | Company C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cash | – | 160 | – |
| Receivables | 300 | – | – |
| Inventory | – | – | 400 |
| Current Assets | 300 | 160 | 400 |
| Current Liabilities | 200 | 110 | 180 |
| Current Ratios | 1.5 | 1.45 | 2.22 |
Please accept – The devil is in the details :-)
Company C has all of its current assets as Inventory. For paying the short term debt, company C will have to move the inventory into sales and receive cash from customers. Inventory takes time to be converted to Cash. The typical flow will be Raw Material inventory -> WIP Inventory WIP inventory (Work-in-Progress) are goods which are in different stages of production. WIP inventory includes materials released from the inventory for the process but not yet completed. The accounting system accounts for the semi-finished goods in this category. read more -> Finished goods Inventory -> Sales Process takes place -> Cash is received. This cycle may take a longer time. As Inventory is less than receivables or cash, the calculated current ratio of 2.22x does not look too great this time.
Company A, however, has all of its current assets as Receivables. For paying off the short term debt, company A will have to recover this amount from its customers. There is a certain risk associated with nonpayments of receivables.
However, if you look at Company B now, it has all cash in its current assets. Even though it's ratio is 1.45x, strictly from the short term debt repayment perspective, it is best placed as they can immediately pay off their short term debt.
Colgate's Current Ratio
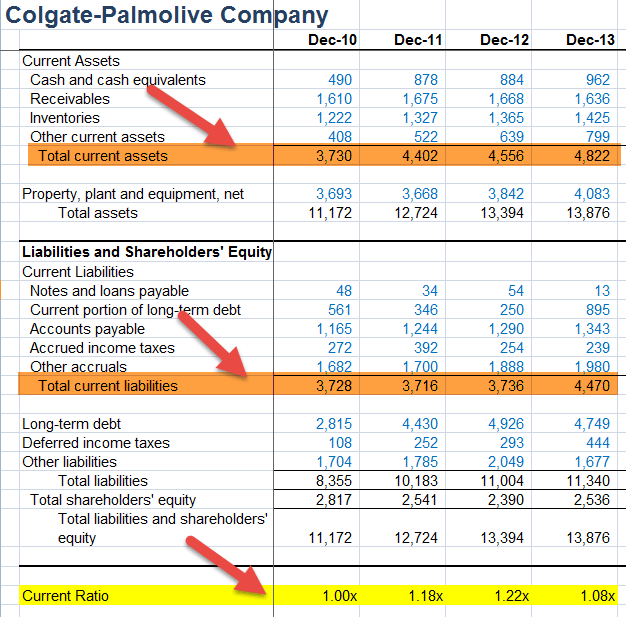
The Current Ratio is calculated as Current Assets of Colgate divided by the Current Liability of Colgate. For example, in 2011, Current Assets was $4,402 million, and Current Liability was $3,716 million.
= 4,402/3,716 = 1.18x
Likewise, we calculate the Current Ratio for all other years.
The following observations can be made with regards to Colgate Ratios –
This ratio increased from 1.00x in 2010 to 1.22x in the year 2012.
- The primary reason for this increase is built-up of cash and cash equivalents Cash and Cash Equivalents are assets that are short-term and highly liquid investments that can be readily converted into cash and have a low risk of price fluctuation. Cash and paper money, US Treasury bills, undeposited receipts, and Money Market funds are its examples. They are normally found as a line item on the top of the balance sheet asset. read more and other assets from 2010 to 2012. In addition, we saw that the current liabilities were more or less stagnant at around $3,700 million for these three years.
- We also note that its ratio dipped to 1.08x in 2013. The primary reason for this dip is the increase in the current portion of long term debt Current Portion of Long-Term Debt (CPLTD) is payable within the next year from the date of the balance sheet, and are separated from the long-term debt as they are to be paid within next year using the company's cash flows or by utilizing its current assets. read more to $895 million, thereby increasing the current liabilities.
Seasonality & Current Ratio
It should not be analyzed in isolation for a specific period. We should closely observe this ratio over a period of time – whether the ratio is showing a steady increase or a decrease. In many cases, however, you will note that there is no such pattern. Instead, there is a clear pattern of seasonality in Current Ratios. Take, for example, Thomas Cook.
I have compiled below the total current assets Current assets refer to those short-term assets which can be efficiently utilized for business operations, sold for immediate cash or liquidated within a year. It comprises inventory, cash, cash equivalents, marketable securities, accounts receivable, etc. read more and total current liabilities of Thomas Cook. You may note that this ratio of Thomas Cook tends to move up in the month of September Quarter.
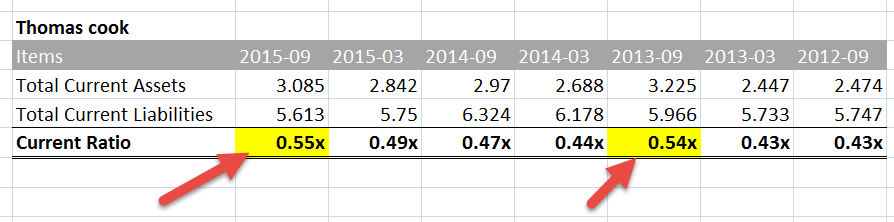
Seasonality is normally seen in seasonal commodity-related businesses where raw materials like sugar, wheat, etc. are required. Such purchases are done annually, depending on availability, and are consumed throughout the year. Such purchases require higher investments (generally financed by debt), thereby increasing the current asset side.
Automobile Sector Current Ratio
So as to give you an idea of sector ratios, I have picked up the US automobile sector.
Below is the list of US-listed automobile companies with high ratios.
| S. No | Company Name | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ferrari | 4.659 |
| 2 | Supreme Industries | 3.587 |
| 3 | Ford Motor | 3.149 |
| 4 | SORL Auto Parts | 3.006 |
| 5 | Fuji Heavy Industries | 1.802 |
| 6 | Sime Darby | 1.71 |
| 7 | Isuzu Motors | 1.603 |
| 8 | Nissan Motor | 1.588 |
| 9 | Mitsubishi Motors | 1.569 |
| 10 | Toyota Industries | 1.548 |
Please note that a Higher ratio may not necessarily mean that they are in a better position. It could also be because of –
- slow-moving stocks or
- lack of investment opportunities.
- Also, the receivables collection could also be slow.
Below is the list of US-listed automobile companies with low ratios.
| S. No | Company Name | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Saleen Automotive | 0.0377 |
| 2 | BYD Co | 0.763 |
| 3 | Greenkraft | 0.7684 |
| 4 | BMW | 0.935 |
If the ratio is low due to the following reasons, it is again undesirable:
- Lack of sufficient funds to meet current obligations and
- A trading level beyond the capacity of the business.
Limitations
- It does not focus on the breakup of Assets or Asset Quality. The example that we saw earlier, Company A (all receivables), B (all cash), and C (all inventory), provide different interpretations.
- This ratio in isolation does not mean anything. It does not provide an insight on product profitability Profitability refers to a company's ability to generate revenue and maximize profit above its expenditure and operational costs. It is measured using specific ratios such as gross profit margin, EBITDA, and net profit margin. It aids investors in analyzing the company's performance. read more etc.
- This ratio can be manipulated by management. An equal increase in both current assets and current liabilities Current Liabilities are the payables which are likely to settled within twelve months of reporting. They're usually salaries payable, expense payable, short term loans etc. read more would decrease the ratio, and likewise, an equal decrease in current assets and current liabilities would increase the ratio.
Video
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to what is current ratio and its meaning. Here we discuss the formula to calculate the current ratio along with its interpretation in accounting. You may learn more about financial analysis from the following articles –
- Acid Test Ratio
- Current Ratio vs. Quick Ratio
- Cash Ratio Meaning
how to find current ratio
Source: https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/current-ratio/
Posted by: breedingalliat.blogspot.com

0 Response to "how to find current ratio"
Post a Comment